
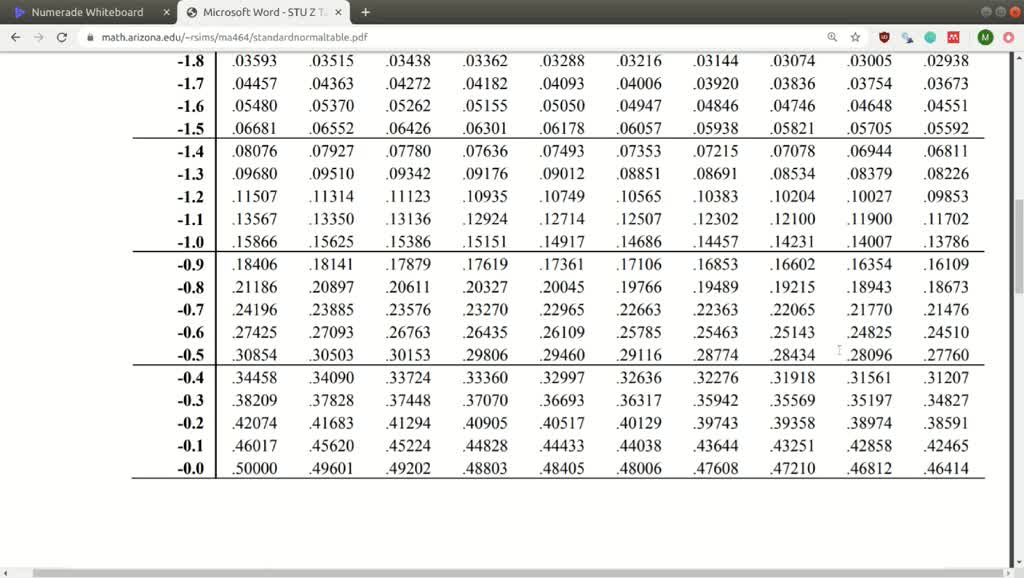
\(x\) is the value we are standardizing, \(\mu\) is the mean, and \(\sigma\) is the standard deviation.A z-table, also called standard normal table, is a table used to find the percentage of values below a given z-score in a standard normal distribution.Ī z-score, also known as standard score, indicates how many standard deviations away a data point is above (or below) the mean.Ī positive z-score implies that the data point is above the mean, while a negative z-score indicates that the data point falls below the mean. The formula for calculating a Z-value is: Z-values express how many standard deviations from the mean a value is. The standard normal distribution is also called the 'Z-distribution' and the values are called 'Z-values' (or Z-scores). Typically, probabilities are found by looking up tables of pre-calculated values, or by using software and programming. The functions for calculating probabilities are complex and difficult to calculate by hand.
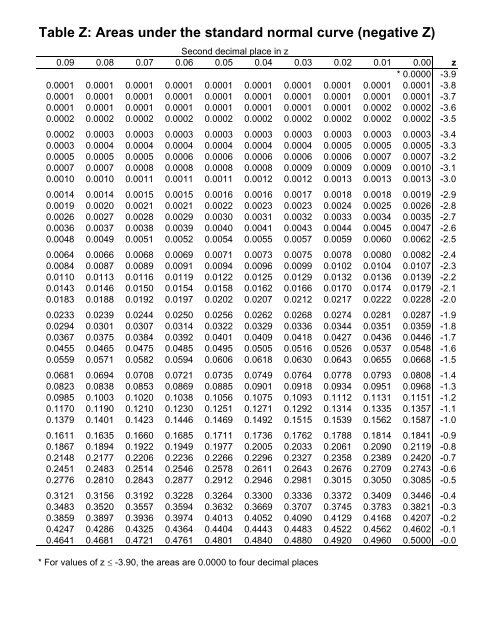
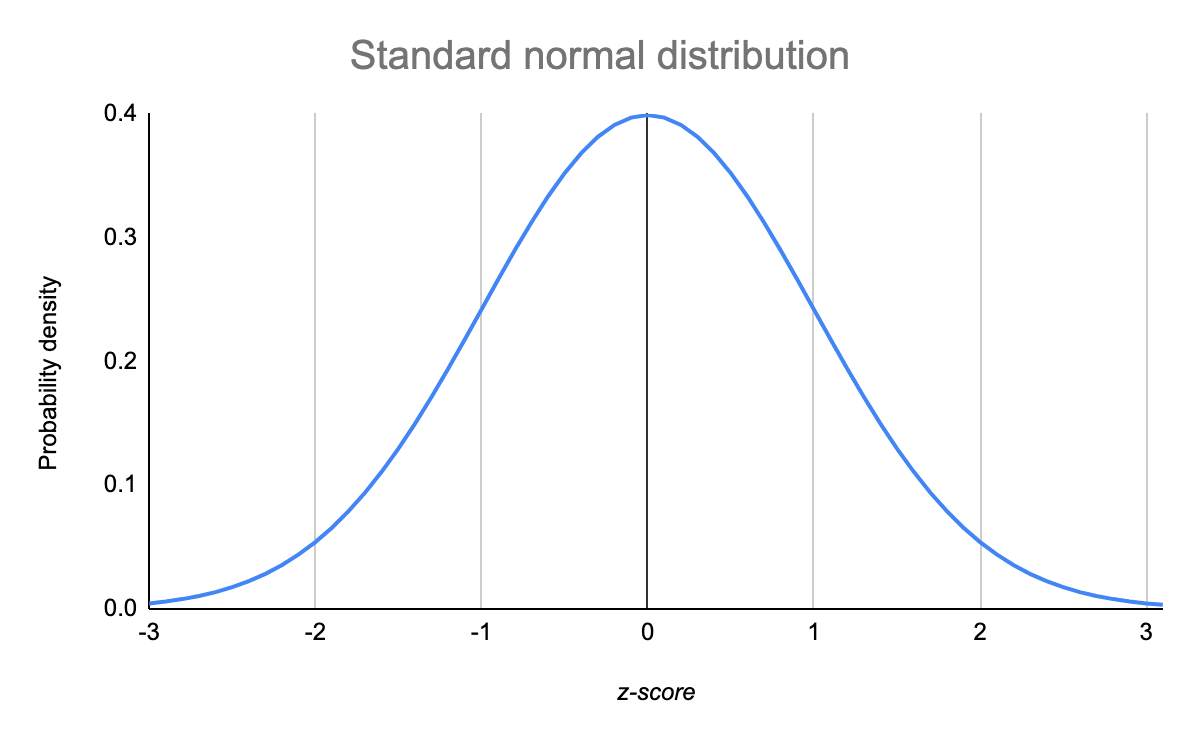
Standardizing makes it easier to calculate probabilities. Here is a graph of the standard normal distribution with probability values (p-values) between the standard deviations: The standard normal distribution is used for: Standardizing normally distributed data makes it easier to compare different sets of data. Normally distributed data can be transformed into a standard normal distribution. The standard normal distribution is a normal distribution where the mean is 0 and the standard deviation is 1. Stat Reference Stat Z-Table Stat T-Table Stat Hypothesis Testing Proportion (Left Tailed) Stat Hypothesis Testing Proportion (Two Tailed) Stat Hypothesis Testing Mean (Left Tailed) Stat Hypothesis Testing Mean (Two Tailed)
Inferential Statistics Stat Statistical Inference Stat Normal Distribution Stat Standard Normal Distribution Stat Students T-Distribution Stat Estimation Stat Population Proportion Estimation Stat Population Mean Estimation Stat Hypothesis Testing Stat Hypothesis Testing Proportion Stat Hypothesis Testing Mean Statistics Tutorial Stat HOME Stat Introduction Stat Gathering Data Stat Describing Data Stat Making Conclusions Stat Prediction & Explanation Stat Populations & Samples Stat Parameters & Statistics Stat Study Types Stat Sample Types Stat Data Types Stat Measurement Levelsĭescriptive Statistics Stat Descriptive Statistics Stat Frequency Tables Stat Histograms Stat Bar Graphs Stat Pie Charts Stat Box Plots Stat Average Stat Mean Stat Median Stat Mode Stat Variation Stat Range Stat Quartiles and Percentiles Stat Interquartile Range Stat Standard Deviation


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
